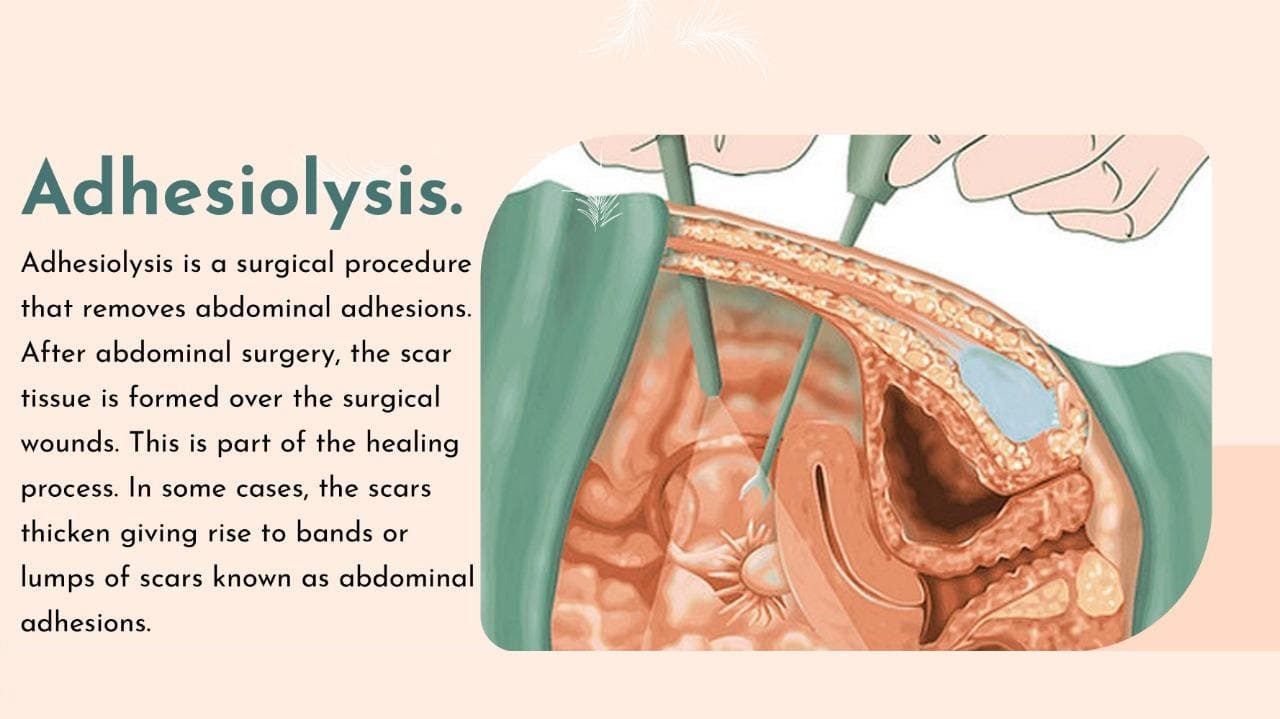
Abdominal Adhesiolysis Surgery
27
Jan
2022
What is Abdominal Adhesiolysis?
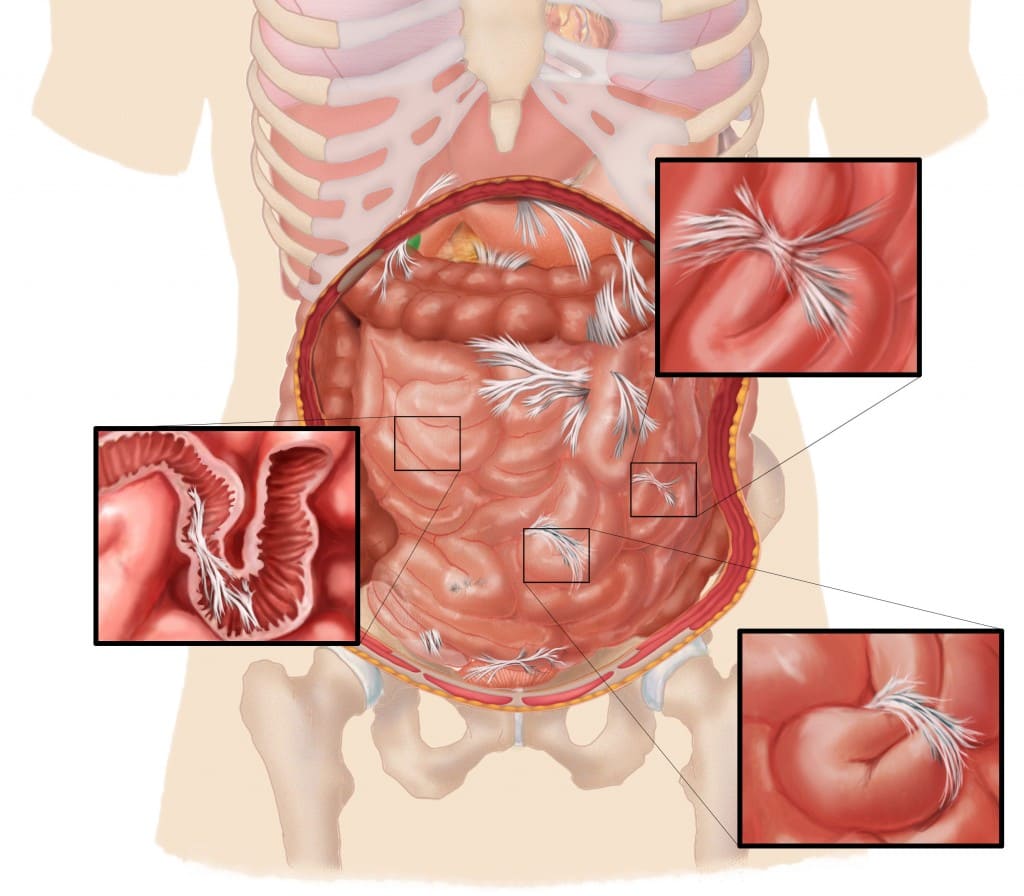
Adhesions are lumps of scar tissue that develop inside your body. Previous surgeries cause about ninety percent of abdominal adhesions. They could also develop from trauma, infections, or conditions that cause inflammation.
Adhesions could also develop on the organs and cause organs to stick together. Many people with adhesions do not experience any symptoms, but some people might have discomfort or digestive problems.
Abdominal adhesiolysis is a kind of surgery that removes these adhesions from your abdomen.
Adhesions do not show up on conventional imaging tests. Rather, doctors usually discover them during diagnostic surgery when investigating symptoms or treating another condition. If the doctor finds adhesions, adhesiolysis might be performed.
In this article, we are going to look at who may benefit from abdominal adhesiolysis surgery. We will also look at the procedure and what specific conditions it might be used to treat.
When is laparoscopic adhesiolysis performed?
Abdominal adhesions usually do not cause noticeable symptoms. Adhesions usually go undiagnosed because they are not visible with current imaging methods.
However, for some people, they could cause chronic pain and abnormal bowel movements.
If your adhesions are causing problems, laparoscopic adhesiolysis could remove them. It is a minimally invasive procedure. With laparoscopic surgery, your surgeon will make a tiny incision in your abdomen and insert a laparoscope to locate and remove the adhesion.
A laparoscope is a long slim tube that contains a camera and light.
Laparoscopic adhesiolysis might be used to treat the following conditions:
Intestinal blockages
Adhesions could cause problems with digestion and even block the intestines. The adhesions could pinch off part of the intestines and cause a bowel obstruction. The obstruction might cause:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- An inability to pass gas or stool
Infertility
Adhesions could cause female reproductive problems by obstructing the ovaries or fallopian tubes.
They could also cause painful intercourse for some people. If your doctor suspects adhesions are causing your reproductive issues, they might recommend surgery to remove them.
Pain
Adhesions could sometimes cause pain, particularly if they are blocking the bowels. If you have abdominal adhesions, you might also experience the following symptoms along with your pain:
- Nausea or vomiting
- Swelling around your abdomen
- Dehydration
- Cramps
What is open adhesiolysis?
Open adhesiolysis is another alternative to laparoscopic adhesiolysis. During open adhesiolysis, a single incision is made through the midline of your body so your doctor could remove the adhesions from your abdomen. It is more invasive than laparoscopic adhesiolysis.
What causes adhesions?
Abdominal adhesions could form from any type of trauma to your abdomen. However, they are most commonly a side effect of abdominal surgery.
Adhesions caused by surgery are more likely to cause symptoms than other kinds of adhesions. If you do not feel symptoms, they generally do not need to be treated.
Infections or conditions that cause inflammation could also cause adhesions, like:
- Crohn’s disease
- Endometriosis
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
- Peritonitis
- Diverticular disease
Adhesions usually form on the inner lining of the abdomen. They could also develop between:
- Organs
- Intestines
- Abdominal wall
- Fallopian tubes

The procedure
Before the procedure, your doctor will likely perform a physical examination. They might also order a blood or urine test and request imaging to help rule out conditions with similar symptoms.
Before the surgery
Prepare for your surgery by arranging a drive home from the hospital after your procedure. You will also likely be advised to avoid eating or drinking on the day of your surgery. You might also need to stop taking specific medications.
During the surgery
You will be given general anesthesia so you do not feel any pain.
Your surgeon will make a tiny incision in your abdomen and use a laparoscope to locate the adhesion. The laparoscope will project images onto a screen so your surgeon can find and cut out the adhesions.
In total, the surgery will take between one and three hours.
Complications
The surgery is minimally invasive, however, there are still possible complications, including:
- Injury to organs
- Worsening of adhesions
- Hernia
- Infections
- Bleeding
Other types of adhesiolysis
Adhesiolysis surgery might be used to remove adhesions from other parts of your body.
Pelvic adhesiolysis
Pelvic adhesions could be a source of chronic pelvic pain. Surgery generally causes them, but they could also develop from an infection or endometriosis.
Hysteroscopic adhesiolysis
Hysteroscopic adhesiolysis is a surgery that removes adhesions from within the uterus. Adhesions could cause pain and complications with pregnancy. Having adhesions in the uterus is also known as Asherman syndrome.
Epidural adhesiolysis
After spinal surgery, the fat found between the outer layer of the spinal cord and vertebrae could be replaced with adhesions made of tough fibrotic tissue that could irritate your nerves.
Epidural adhesiolysis helps to remove these adhesions. Epidural adhesiolysis is also called the Racz catheter procedure.
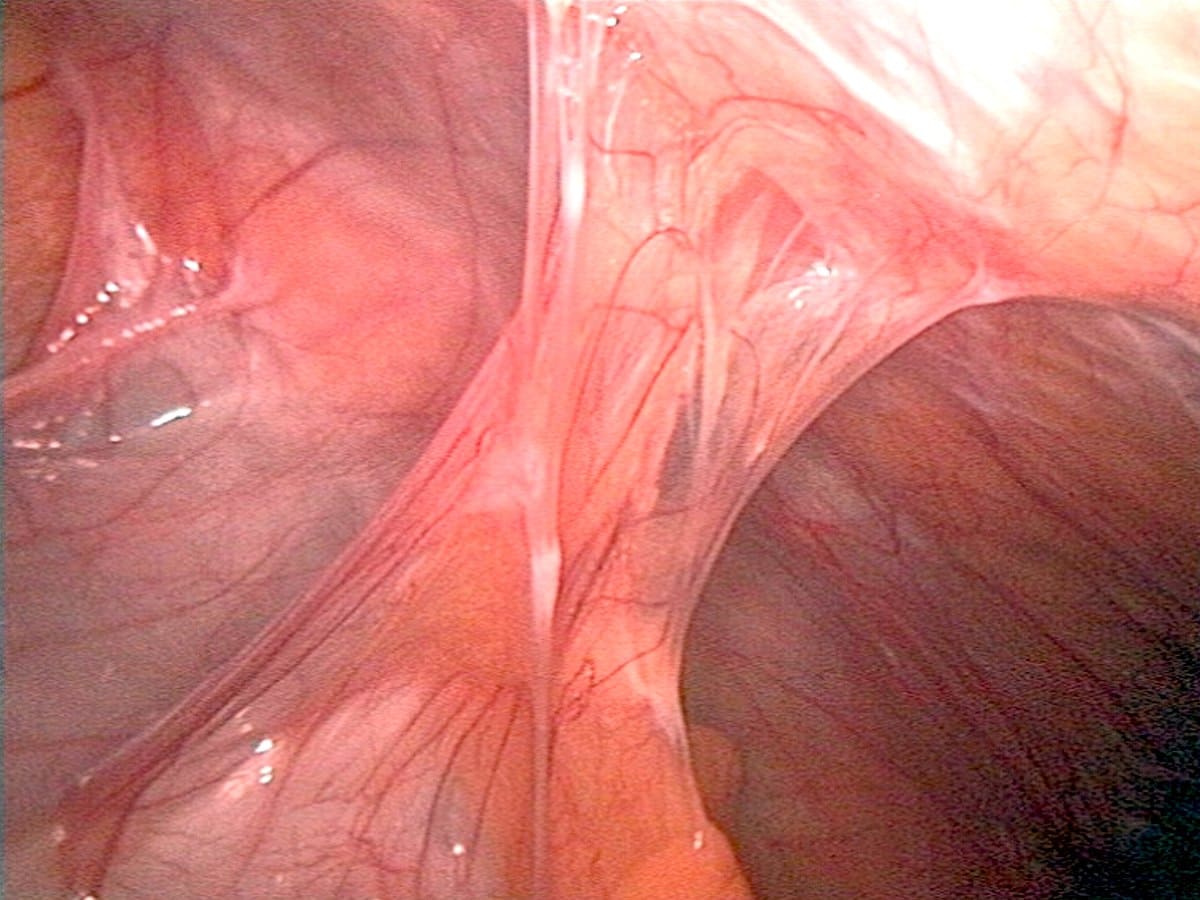
Peritoneal adhesiolysis
Peritoneal adhesions develop between the inner layer of the abdominal wall and other organs. These adhesions may appear as thin layers of connective tissue consisting of nerves and blood vessels.
Peritoneal adhesiolysis is intended to remove these adhesions and improve symptoms.
Adnexal adhesiolysis
An adnexal mass is growth around the uterus or ovaries. They are usually benign, but in some cases, they might be cancerous. Adnexal adhesiolysis is a surgical method of removing these growths.
Adhesiolysis recovery time
You might have discomfort around your abdomen for about two weeks. You should be able to return to regular activities in two to four weeks. It might also take several weeks for your bowel movements to become regular again.
To improve your recovery from abdominal adhesiolysis surgery, you should:
- Get plenty of rest.
- Avoid intense physical activity.
- Speak to your doctor about foods you should avoid.
- Wash the surgical wound every day with soapy water.
- Call your doctor or surgeon immediately if you have signs of an infection, like fever or redness and swelling at the incision area.
Takeaway
Many people with abdominal adhesions do not experience any symptoms and do not need treatment.
However, if your abdominal adhesions are causing pain or digestive problems, your doctor might recommend abdominal adhesiolysis to remove them.
Getting an appropriate diagnosis is the best way to find out if your discomfort is caused by adhesions or some other condition.
Hill Regional (HRH) Hospital is here to assist all your medical needs with specialists and surgeons trained and experienced in the most advanced treatments. Our highly qualified doctors, nurses, and administrators are dedicated to caring for you with compassion in our state-of-the-art facilities.
Call us on 254-580-8500 to book an appointment with our specialist doctors.