What is Back Pain?
07
July
2021
Back pain is a common type of ache that could hit one spot or spread all across the back which could affect the neck and the hips. Your back pain could be resulting from muscular, nervous, or/and from other causes that trigger pain such as arthritis. In other terms, back pain could be resulting from inadequate physical activity, injuries, or other medical conditions that are due to infections and inflammations.
Given that the back is the main support that keeps the human body erect, the pain that attains that region could lead to the disruption of daily and mundane activities like walking, running, standing, or even sitting. Older people tend to develop back pain quickly and easily due to many conditions such as degenerative disk disease, the decrease in muscle mass, and the general degeneration of muscle density.
What you need to know about your back
The back is formed from very important structural bones and muscles that keep the human body standing straight. Given the importance and the sensitivity of these structural networks and functions of the back, it is important to note that any injury, spasm, or medical condition could cause intense pain that spreads across the entirety of that area. Here is what you need to know about the back’s anatomy:
-
The Spine
The spinal canal is formed of 33 disk-like bones known as vertebrae which not only erect the human back, but also protects the spinal cord located inside the spine. Each vertebra is located between disks that cushion and protect these bones from any shock.
-
The spinal cord
The spinal cord consists of nerves that are located inside of the spine, and that run from the lower back and up to the neck. The spinal cord nerve allows the body to sense heat, cold, and vibrations. It regulates blood pressure, body temperature, and heart rate. It also helps with other body functions like urinating, breathing, and controlling bowel movement.
-
Back muscles
Superficial muscles: These muscles allow the movement of the limbs.
Intermediate muscles: These muscles support respiration as they connect to the ribs.
Intrinsic muscles: These muscles allow movements like bending and rotating. They are located deeper into the back.
What are the Symptoms of Back Pain?
Back pain can be felt like an ache in the muscles, like a stabbing or a burning sensation that radiates throughout the back. It can also radiate into the abdomen, up the neck and down to the legs. Home treatment and adequate exercise usually decreases the intensity of the pain and cures the minimal causes that are triggering back pain. however, it is best to visit a healthcare professional in case the following symptoms are persistent:
The pain is long lasting and persistent
The pain has been consistent for more than a few days
The pain radiates down one or both legs
The pain causes tingling, weakness, and/or a sensation of numbness in one or both legs
The pain is accompanied with unintentional weight loss
The condition can be serious in case of experiencing the following symptoms:
Uncontrollable bowel movement
The pain is accompanied by a fever
The pain is due to a fall, an accident, or a blow that could have caused broken bones, or fractured bones.
What Causes Back Pain?
There are many conditions that could trigger pain all across the back or in a specific part of the back. Upper back pain can be triggered by complications such as disorders of the aorta, spine inflammation or even tumors in the chest or the spine. Lower back pain on the other hand, could be triggered by the herniation of the disks between the vertebrae, injuries in the ligaments around the spine, rupture in the lower back muscles, Sciatica, and other causes.
Here some conditions and complications that cause back pain:
-
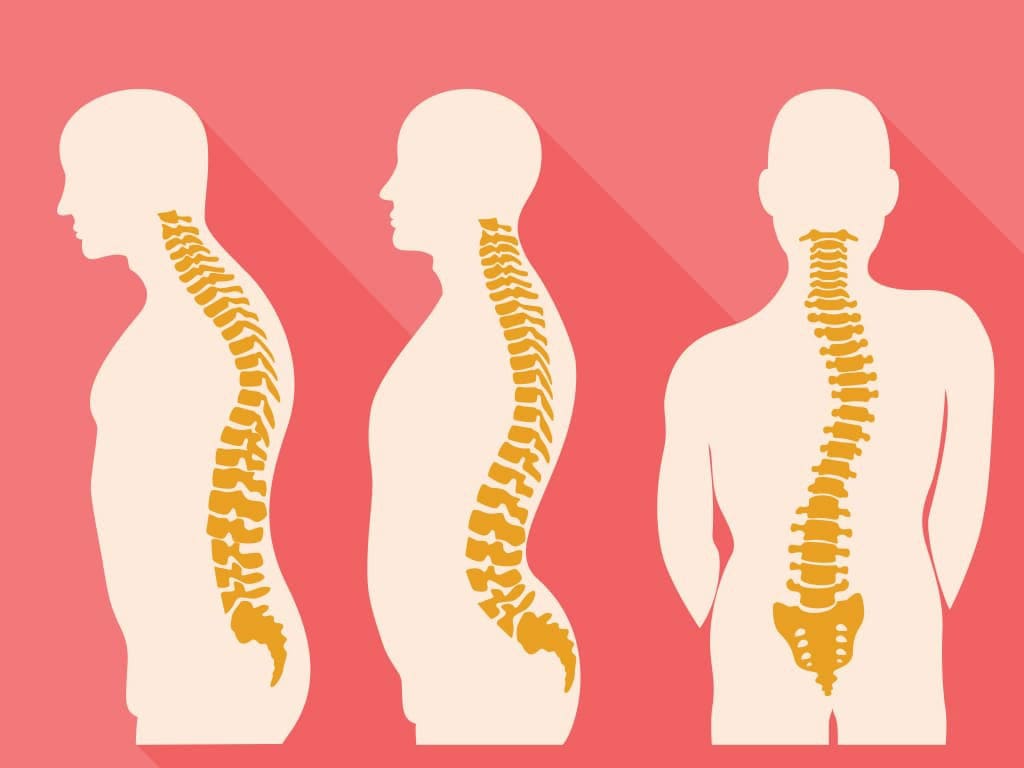
Abnormal spinal curves
Kyphosis of the thoracic spine: This condition is also known as “hunchback”. It causes an outward curvature in the upper back.
Scoliosis: This condition causes a sideways curvature in the spine which causes it to develop an S or a C shape.
Lordosis of the lumbar spine: This condition causes the formation of an abnormal arch in the lower back.
-
Bone fragility
Osteoporosis: This condition causes the bones to lose density, therefore becoming fragile. People above 50 are more likely to develop Osteoporosis which triggers back pain, possible bone fractures and structural irregularities.
-
Cartilage issues
Intervertebral disk degeneration: This condition refers to the degeneration of the disks located between the spine’s vertebrae. The decrease in the protective cushioning that these disks provide triggers pain.
Osteoarthritis: This condition causes the bones to rub against each other due to the degeneration of cartilage. This condition therefore affects the joints of the spine leading to discomfort, stiffness, and severe pain.
-
Nerve-related issues
Sciatica: The compression of the sciatic nerve causes pain. The pressure that compresses the nerve roots leads to irritation, pain, a tingling sensation or even numbness in the lower back. The pain could radiate to the buttocks and the legs.
-
Muscular issues
Muscle strains: Lifting heavy objects, being subject to a sudden or traumatic hit, or making a sudden and harmful move, can lead to muscle strains. These strains can cause muscle spasms and severe pain that radiates across the back.
-
Injuries
Burst fracture: Due to a sudden and traumatic accident, a violent type of bone fracture can happen leading to bone shattering and causing damages to the spinal cord.
Fracture-dislocation: Tissue damage as well as ligament damage can lead to severe fractures in the spine, also causing harm to the spinal cord.
-
Other complications
Kidney problems: Kidney stones and kidney infections can cause pain in the back.
Vertebral tumor: This tumor affects neurological functions. The tumor grows within the bones and causes pressure on the spinal cord.
How to Diagnose the Cause of Back Pain?
After carrying out physical examinations, the healthcare professional should be able to diagnose the causes of the pain.
Some imaging tests and other examination checks can be carried out to spot the exact reasons, the location and the triggers of the pain. Here are some tests that might be recommended:
X-Ray: Detecting the alignment of the spine requires an X-ray. Detecting arthritis, and bone fractures also require an X-ray test.
Bone scans: Bone scans can detect osteoporosis, as well as the presences of any bone tumor.
MRI scans: An MRI scan detects abnormalities linked to the ligaments, the tendons, the muscles, the nerves, the blood vessels, and other tissues.
EMG test: This test records the electrical impulses of the nerves.
The healthcare professional might redirect you to a:
Chiropractor: Who will run physical examinations and observations, through palpitation and touch.
Physical therapist: Who will help detect any joint issue.
Osteopath: Who will detect any mobility complications.
How to Prevent Back Pain from Occurring?
Preventing back pain is a process that requires taking care of your general health, and that of your bones and muscles more specifically. Here are some measures that you can take into consideration to prevent back pain from developing or intensifying:
Exercising
Building muscles flexibility and strength
Maintaining a healthy weight
Avoiding smoking and other addictive behaviors that impact your general health
Do not spend long hours without moving
Sit correctly
Lift objects correctly
Avoid lifting heavy objects
Stand straight and avoid slouching at any time
Choose exercises that help improve your back muscles’ strength and flexibility such as swimming
How to Treat Back Pain?
For mild and minor pain, exercising and following personalized physical therapy sessions can help reduce and then eliminate the pain. However, for more developed conditions, here are some treatment methods and procedure the healthcare professional could assign to you the following:
-
Home treatment
Over-the-counter medications can help reduce the pain. However, in case back pain is not reduced with pain-relief medications, the healthcare professional might prescribe narcotics that should be consumed for a short period of time and that should be monitored by a healthcare professional.
Cortisone injections: anti-inflammatory drugs can be injected into the epidural space. It helps reduce inflammation around the affected nerve roots.
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation: this treatment is prescribed to people with chronic back pain. The Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation machines deliver minor electric pulses into the back. This treatment helps reduce the pain.
Surgery: there are many surgical procedures for back conditions, such as:
Artificial disk: the replacement of the damaged disks with artificial ones
Partially removing a vertebra: a small section of a vertebra is removed in case it was pinching the spinal cord
Fusion: this surgery consists of fusing two vertebrae together instead of separating them with a disk implantation.
Discectomy: in case a disk was irritating a nerve, this disk will be partially removed.
If you or anyone you know is suffering from severe back pain, call us today on (469) 562 4188 to book an appointment with our expert doctors.