Constipation – Overview, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
09
July
2021
Constipation happens when the bowel movements are less frequent, and there's difficulty in passing stools. This usually happens because of a change in diet or imbalanced fiber intake
Overview
The definition of Constipation has less than three bowel movements in a week. Therefore, how often a person uses the toilet varies from one person to another. Some people have bowel movements many times a day, while others only have one or two times a week. Bowel movements are unique for each person, no matter the pattern, as long as the person doesn't stay too long in a way. Therefore, one pattern is critical. The more difficult it gets for stool to pass, the longer the person will use the toilet. Essential key points when understanding constipation are the following:
Feeling of not fully emptying the bowels.
Painful bowel movement with difficulty in passing stools.
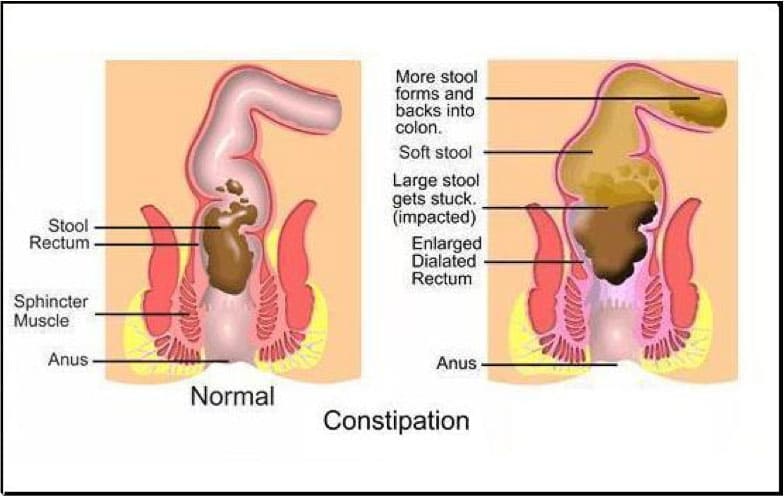
Hard and dry stools (refer to the image below)
How Does Constipation Happen?
Constipation occurs because your colon absorbs too much water from waste which dries out the stool making it difficult to consistency and tough to push out of the body.
To back up a bit, as food moves typically through the digestive tract, vitamins are absorbed. The partly digested meals (waste) that stay strikes from the small gut to the large intestine, also known as the colon. The colon absorbs water from this waste, which creates a firm rely on referred to as stool. If you have Constipation, meals may pass too slowly through the digestive tract. This gives the colon greater time – too much time – to soak up water from the waste. The stool will become dry and hard to push out.
How common is Constipation?
Constipation is one of the most constant complaints around the globe. More than 2.5 million people check with their doctors every year because of Constipation. People of all ages can experience situations of Constipation, such as:
Having neurological and digestive disorders.
Older people are less active and usually struggle with slow metabolism and less muscle contraction making them more affected by Constipation.
Being a woman, specifically during pregnancy and after childbirth, due to changes in hormones. Even during pregnancy, the baby squeezes the intestines making the passage of stool slower.
Not eating foods high in fiber to keep food moving through the intestines.
Can Constipation cause other Problems?
Some complications are caused by Constipation that usually happens when the patient doesn't have a regular bowel movement, complications such as:
Pelvic floor muscle damage that strains the bowel from moving. These muscles help in controlling the bladder. Long-term straining can cause leakage from the bladder, which is called "stress urinary incontinence."
A condition called "hemorrhoids" is having swollen and inflamed veins in the rectum.
A stool pile up in the anus and rectum. This is a condition called "fecal impaction."
Tears in the anus lining from hard stools trying to pass through called "anal fissures."
A condition called "diverticulitis" is an infection in pouches that form the colon from stool that infected and stuck.
Causes of Constipation
The causes for Constipation are numerous; each can be categorized into three essential parts such as pregnancy, medications, or lifestyle choices.
-
Lifestyle Choices:
Stress.
Resisting bowel movement urges.
Eating significant amounts of cheese or milk.
Eating foods that are low in fiber.
Not drinking enough water.
Not having enough exercise.
Changes in the routine, such as going to bed at different timings, changes in eating habits, or traveling.
-
Medications that cause Constipation:
Anti-nausea medications such as Zofran.
Seizure medications.
Psychiatric medications.
Vital pain killer medicines.
Anti-inflammatory drugs.
Antidepressants.
Antacids that contain aluminum or calcium.
Allergy medications.
Some blood pressure medications.
Some several drugs and medications cause Constipation. It is essential to ask the doctor for questions or concerns.
-
Health conditions that cause Constipation:
Pregnancy.
Organ diseases such as scleroderma, lupus, amyloidosis.
Lazy bowel syndrome where the colon contracts in a lazy manner while retaining stool.
Endocrine problems, such as underactive thyroid gland, diabetes, uremia, hypercalcemia.
Irritable bowel syndrome.
Diverticular disease.
Outlet dysfunction constipation, where there is a defect in the coordination of the pelvic floor muscles. These muscles support the organs in the pelvis and the lower abdomen that are needed in helping to release the stool from the body.
Neurological disorders such as spinal cord injuries, strokes, Parkinson's disease, and multiple sclerosis.
Symptoms
Constipation symptoms can include:
Having the feeling that the person didn’t empty their bowels after movement.
Feeling nauseous and bloated.
Having fewer bowel movements in a week.
Stools are dry, lumpy, and hard.
Stools are painful and hard to pass.
Having stomach aches or cramps.
Tests and Diagnosis
Getting in contact with the doctor about the lack of bowel movements is very important. Doctors are trained health professionals; there is no shame in discussing unpleasant topics with doctors. To diagnose the cause, doctors first ask questions about the medical history, lifestyle, routines, and bowel movements. These questions usually include:
Have you ever had a colonoscopy?
Does anyone in your family have Constipation or disease of the digestive tract or a history of colon cancer?
Have you had any previous digestive tract surgeries?
Have you lost or gained weight recently?
How often do you have a bowel movement?
Have you ever seen blood in the toilet after releasing stool?
What is your exercise routine?
The doctor will also perform a physical exam that includes checking for vital signs, where the doctor will use a stethoscope to listen to the sounds of the abdomen, and it will also be touched for pain, tenderness, or swelling. It is critical to consider that the doctor will also have to perform a rectal exam, which is a finger exam inside the rectum. This is a fast check for problems, swelling, or masses that can felt by the finger.
Doctors also usually order tests if the condition is very intense. These tests include:
Colonoscopy: This is an internal view of the colon with a scope. During this procedure, a small sample of the tissue is removed to test for cancer or any other issues that might be present.
Imaging tests include computed tomography, MRI, or lower gastrointestinal tract that can be ordered to identify the possible problems causing constipation.
Colorectal transit studies involve consuming small doses of a radioactive substance, whether a pill or a meal. Then tracking the amount of time and its movement in the intestines.
Lab tests: blood and urine tests reveal any signs of anemia, diabetes, or hypothyroidism—stool sampling checks for inflammation, cancer, or infection.
Treatment
Many cases of mild to moderate Constipation are managed at home. Self-care begins with changing what you drink and eat and then make changes accordingly. There are several recommendations and home remedies that can be used, such as:
Drinking two to four glasses of water every day and avoiding caffeine drinks and alcohol because these drinks cause dehydration that can worsen Constipation.
Checking how you sit on the toilet is essential. It would be best to raise your feet while leaning back or squatting to make more effortless bowel movements.
Exercise.
Eat fewer foods that are high in fats, such as eggs, meat, and cheese.
In addition, the doctor will review the medications that you take because some of these supplements might cause Constipation. If they do, the doses should be reduced, or you will be asked to stop taking the supplement. On the other hand, some drugs are available to treat Constipation, which includes lubiprostone, lactulose. The doctor must pick the drug which works best for your condition.
In extreme cases, surgery would be needed to treat Constipation. The doctor might recommend surgery if a problem in the colon causes Constipation. For instance, blockage in the colon, narrowing the intestine, rectum collapse into the vagina, or tear in the anus. Some causes of constipation can be treated through surgery. The patient will also need surgery if cancer was found in the colon or the anus.
Prevention
Some home-based methods can be used to treat Constipation to prevent it from becoming a chronic problem:
Do not wait to move your bowels when you feel the urge.
Treat mild Constipation with dietary supplements like magnesium.
Drink eight glasses of water every day. Avoid drinks that can dehydrate the body, such as coffee and soft drinks.
Eat plenty of foods that are high in fiber. Good sources of fiber are fruits, vegetables, whole grains, cereals, and legumes. Fiber and water can help the colon to pass stool. Many of the fruits high in fiber, like strawberries, have the highest fiber level. Bran is also a great source of fiber. People who are suffering from Constipation must eat between 18 and 30 grams of fiber every day.
It is essential to talk openly with your doctor about bowel movements and discuss any problem concerning you. Constipation might be a temporary issue but might sometimes be a severe condition. Check with your doctor whenever you notice a change in your bowel pattern.
If you or anyone you know is suffering from pain, call us today on (254) 580-8765 to book an appointment with our expert doctors.