Pain in the right side of the body
10
July
2021

Side pain could indicate a wide number of underlying conditions. Diseases, disorders, infections, inflammations, and other health issues that can develop on the right side of the body.
The right area contains half of the body’s systems. Along with muscles, bones, blood vessels tissues, organs, and nerves, this area includes also parts of the skeletal system, muscular system, respiratory system, digestive system, nervous system, cardiovascular system, urinary system, and reproductive systems.
If you feel any pain in your right side it is crucial to locate and identify the reason behind it, which organ can be damaged to thereby move forward.
Different causes that can trigger pain in the right side of the body:
In order to cover the largest number of causes, we have to break down the organs situated on the right side.
-
The skeletal system:
Bone pain can be the result of a trauma, a contusion, or a fall. Whether it’s a small break or a serious fracture, the damage will cause pain and tenderness to the affected area. A break could happen in any bone in the arms, legs, shoulders, clavicles, fingers, toes, back, or even ribs. Another cause of bone pain is bone cancer or cancer that has spread to the bones.
-
The muscular system:
Muscle pain, also known as “Myalgia”, can be due to injuries, infections, inflammations, or diseases. Carrying or lifting a heavy object can cause sprains and strains which are painful and may last for a long time. Sports injuries as well can result in too much pressure on the muscles causing damage. Some infections are the reason behind muscle pain such as the flu, covid-19, or malaria.
When the connective tissues connecting the bones to the muscles get inflamed it is called tendinitis. Tendinitis can occur in any area in your body where a tendon connects muscles, and bones. The most common places are the elbows, knees, wrists and shoulders.
-
The respiratory system:
The right lung can develop multiple problems that should be taken seriously and followed up by a specialist.
Some conditions that could occur in the right lung include:
Costochondritis: an inflammation of the chest. More specifically it’s the inflammation of the cartilage that connects the ribs to the sternum.
Pleurisy: the inflammation of the pleura. (The layer that covers the lungs).
Pneumonia: An infection of the lungs caused by a bacteria or a virus.
Pneumothorax: A collapsed lung.
Pulmonary hypertension: High blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries.
Pulmonary embolism: A blockage, mostly a blood clot, in the pulmonary arteries.
Cancer.
-
The cardiovascular system:
Even though cardiac problems are associated with left side pain, right side pain could also indicate a heart problem. The issue could have spread onto this side or can be related to the right side of the heart.
Common cardiac problems include:
Myocarditis: the inflammation of the heart muscle.
Pericarditis: the inflammation of the sac surrounding the heart.
Both of them have symptoms such as the difficulty of breathing, palpitations, fever, and fatigue, etc. It is imperative to get medical help because these are life-threatening conditions.
Heart attack.
Angina: when the heart is not receiving enough blood flow.
Thoracic aortic aneurysm: the rupture of the aneurysm results in an extremely dangerous excessive bleeding and even death.
-
The digestive system:
The digestive system contains multiple organs that can develop issues or get damaged.
Appendix: if you feel a sharp pain in your abdomen on the right side, one of the reasons could be appendicitis. Appendicitis is the inflammation of the appendix. It can come along with vomiting, fever or, diarrhea. It needs medical help as soon as possible because of the possibility of it rupturing.
-
Liver: Multiple disorders are associated with the liver:
Liver abscess: a pus full mass in the liver.
Hepatitis: the inflammation of the liver.
Cirrhosis: A permanent damage to the liver where scar tissues replace the healthy tissues, stopping your liver from working properly.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: The buildup of fatty tissues with little to no consumption of alcohol.
Liver failure: when the liver is no longer able to function or to perform its function.
Liver cancer.
Pancreas: This organ helps with digestion by producing enzymes as well as helping your body regulate the process of sugar.
Pancreatitis: The inflammation of the pancreas.
Pancreatic cancer.
Intestines: several issues can occur in the intestine: constipation, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), cramps, diarrhea, gas, diverticulitis, colitis, and diseases such as Crohn’s disease or celiac disease.
Spleen: a ruptured spleen lead to internal bleeding and should be immediately treated.
Abdominal aortic aneurysm: AAA is a life-threatening condition.
-
The nervous system:
The nervous system is formed by the central nervous system: the brain and the spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system: the nerves that go through the whole body.
Disorders in the nervous system can have an impact on how your body responds to pain. For example: chronic neuropathic pain is when your body sends signals of pain to your brain without an obvious pain-inducing event or injury.
Pain can also be a sign of a stroke happening or a cerebral hemorrhage: a burst in the blood vessel causing bleeding in the brain and is accompanied by vomiting.
Other disorders include: epilepsy, headache, migraine.
-
The urinary system:
The urinary system is formed by the kidneys, two ureters, the bladder, and the urethra.
What are the complications that could happen with the right-sided organs?
-
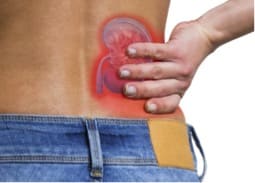
Right kidney pain could indicate:
Kidney stones.
Kidney cancer.
Kidney infarction (the death of kidney tissue due to lack of oxygen).
Kidney infection (pyelonephritis).
Kidney abscess or cyst.
Swollen kidney (hydronephrosis, due to the buildup of urine).
Ureter: Ureteral obstruction is a treatable problem. However, left untreated it can result in serious issues like sepsis and even death.
The bladder:
Cystitis: a bladder infection causing inflammation.
Urinary tract infection (UTI).
Bladder cancer.
Gallstones.
The urethra: pain in the urethra can be due to:
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs).
Irritation or allergies to products (soaps, shower gel).
Trauma to the area.
-
-
The reproductive system:
In Women:
Right ovarian cysts.
Right ovarian torsion.
Right ovarian cancer.
Ovulation pain.
Pelvic inflammatory.
Endometriosis.
Fibrosis.
Ectopic pregnancy.
Blocked fallopian tube.
Ruptured fallopian tube.
Breast cancer.
Menopause.
Sore breasts due to the change of hormones.
Breast cyst.
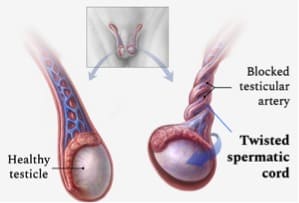
In Men:
Testicular torsion.
Prostate cancer.
Epididymis.
Trauma to the testicles or the penis.
STI (sexually transmitted infections).
How to treat the pain?
Treating the pain depends completely on the diagnosis. Each area has itstreatment, each organ can responds differently.
Some common treatments include:
Pain relief medicine if it’s a mild condition.
Surgery for complicated cases such as kidney stones, ovarian or testicular torsion, appendicitis, ruptured spleen, fractures, etc.
Chemotherapy or radiation therapy for cancer cases.
Antibiotics for infections.
Monitoring for some cases that may be able to resolve on their own like pneumothorax.
Clot-busting drugs, blood thinners, or drugs that open closed arteries for some cases of chest pain.
Physical therapy for strains or after surgery.
Symptoms that you should get checked by a doctor:
If the pain is bearable and went away in a few hours it may be a harmless issue. However, if you experience these symptoms, you shouldn’t wait to call your doctor:
Severe, unbearable pain.
Vomiting.
Excessive diarrhea.
Yellow skin.
Coughing blood.
Difficulty of breathing.
Loss of consciousness.
Excessive bleeding (especially if pregnant).
Dislocated bones.
Burning sensation in the chest.
Pain when peeing.
Chest pain irradiating to the arm, shoulder, back, or jaw.
Fever that isn’t responding to medicine.
Sudden, unexplained weight loss.
Your bowel movement has changed.
Pain following a concussion or a trauma.
Blood in the urine of the stool.
How to diagnose the pain?
In order to diagnose the pain, the doctor will first examine you. Palpating your abdomen, your chest, the painful area to check for sensitivity, masses, bruises, moles, etc…
He may also take a look at your nose, throat, and ears, listen to your lungs and heart using a stethoscope, checking your neck or your limbs (checking if they are swollen).
A detailed history is requested from the patient or the patient’s family, including medications, any known diseases, lifestyle activities, what was the patient doing when the pain started, he may be asked to describe the pain, if it has occurred before, any previous surgery, family history of health conditions or known allergies.
After examination, he may request tests to help with the diagnosis:
Blood tests.
Urine tests.
Stool samples.
Throat swabs.
Biopsies.
Imaging can also be needed:
X-rays: mostly for fractures or pulmonary issues.
Ct scans: a fast way to take a better look at the internal organs.
Ultrasounds: used most often to diagnose genital disorders or to confirm pregnancy.
MRIs: used to take a more detailed picture of the concerned organ and to detect abnormalities.
Endoscopy: inserting a long tube with a camera into the throat and the esophagus to look for causes of pain rebel to treatment or bleeding.
Sometimes exploratory surgery is done after all the tests appear to be normal but the pain is consistent. This surgery is also done in case of cancer to take a better look at the spread of it in the organs.
If you or anyone you know is suffering from pain, call us today on (469) 562 4188 to book an appointment with our expert doctors.